How AI Detectors Work: What They Look For and How Accurate They Are in 2026
Introduction
By 2026, the internet has effectively become a hall of mirrors. You are scrolling through social feeds, reading academic papers, or watching news shorts, but the lingering question remains the same: is this real, or AI? Generative AI has mastered the art of syntax and grammar, yet it leaves behind invisible fingerprints that the naked eye usually misses.
While an LLM is designed to predict the next most likely token to satisfy a prompt, an AI detector operates in reverse engineering mode. It does not "read" for pleasure; it looks for the mathematical smoothness that defines machine generation versus the chaotic, unpredictable nature of human thought. Understanding how AI detectors work is no longer just technical trivia, it is essential for academics verifying authorship, journalists checking sources, and artists protecting their copyright.
What Is AI Detection?
AI detection is the computational analysis of statistical, stylometric, and structural signals used to calculate the probability that a specific piece of content was generated by AI. Detectors don’t "know" facts. AI text detection tools analyze the underlying code of language itself.
When asking how to check if something was written by AI, you're really asking about pattern comparison. A text AI detector scans input against datasets of human and AI writing, identifying deviations from human norms. In 2026, this field has expanded beyond text into multimodal analysis.
Modern detection falls into two categories:
- Textual classifiers focus on linguistics, syntax, and token probability to detect AI text.
- Multimodal detector are designed to answer "is this image AI generated" or whether a video clip contains deepfake artifacts. They analyze pixel distributions, audio waveforms, and frame-to-frame consistency.
The goal isn't just to label something as "Fake," but to provide a confidence score that helps a human make an informed decision about the content's authenticity.
How AI Detectors Work: Core Signals & Models
To understand what do AI detectors look for, we have to look under the hood of the LLMs themselves. LLMs are, fundamentally, probability machines. They want to please you by choosing the words that statistically follow one another most smoothly. But humans are erratic, we use slang, make some strange word choices, vary sentence length abruptly, and we have a "voice." Detectors exploit this difference.
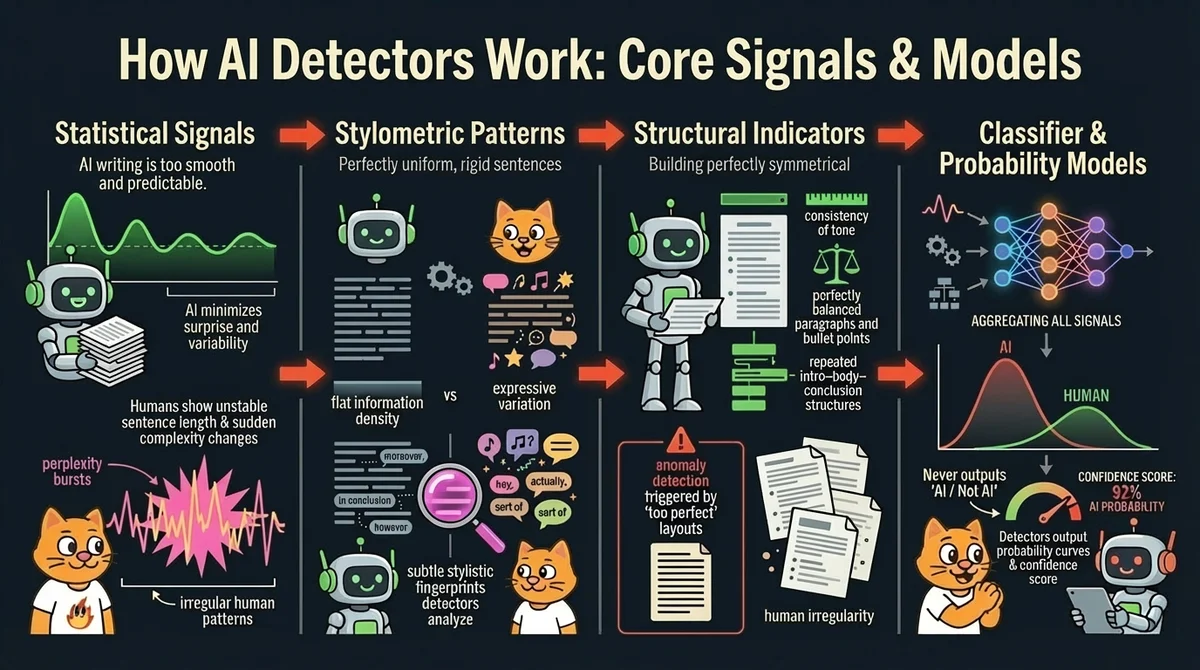
Statistical Signals (Perplexity & Burstiness)
The two most famous metrics in detection are Perplexity and Burstiness.
- Perplexity measures how "surprised" a model is by text..AI models are trained to minimize perplexity, they want to be predictable and clear. Humans create metaphors, choose bright and unpredictable descriptions.
- Burstiness measures variation in complexity. AI writes flat, monotonous sentences with the same complexity. Humans represent "bursts" of creativity. We might write a very long, complex sentence followed immediately by a short one.
Stylometric Patterns
Beyond raw math, detectors analyze style. AI models in 2026 still struggle with the "soul" of writing. They tend to overuse certain transitional phrases (the infamous "In conclusion," "Moreover," or "It is important to note").
Stylometric patterns also cover semantic density. AI tends to be "fluffy", it uses many words to say very little.A detector notices when the information density is unnaturally consistent with quite average word choice. That’s why some academic papers or legal documents can trigger false positives due to similar flatness.
Structural Indicators
Let’s talk about… em dashes, right? We, humans, are messy formatters. We might use a dash here, a semicolon there, or structure a paragraph weirdly for emphasis, or just because we didn't notice this “weirdness” in our writing. AI loves symmetry and order. That is why AI detectors look for perfectly balanced bullet points, identical paragraph lengths, and rigid sandwich structures (Intro-Body-Conclusion) and other signals of anomalous perfection.
So yep, these days perfection is an anomaly that triggers detectors.
Classifiers & Probability Models
All signals feed into a supervised learning model. It doesn't output "Yes/No"—it outputs probability curves. An accurate AI text detector aggregates these signals into a confidence score like "92% probability of AI generation." This means that the model is 92% sure answering the question “is this text AI generated?”. This probability-based approach explains why errors occur.
Accuracy: How Accurate Are AI Detectors in 2026?
How accurate are AI detectors, really? We may say that the answer is context-dependent. Accuracy scales with data volume. If you feed a detector a 50-word tweet, accuracy drops significantly because there isn't enough statistical data to measure burstiness. However, for an 1000-word essay AI detector’s accuracy rates often exceed 98%.
Accuracy varies by modality. Text detection excels on raw GPT-5/Claude output, image analysis reveals pixel-level artifacts with precision, video/audio detection is rapidly improving but still evolving against advancing deepfakes.
Why AI Detectors Make Mistakes (False Positives & False Negatives)
No system is perfect (we don’t like perfection, right?). Detectors have 2 types of mistakes false positive AI detection (accusing a human of using AI) and false negative AI detection (letting AI slip through).
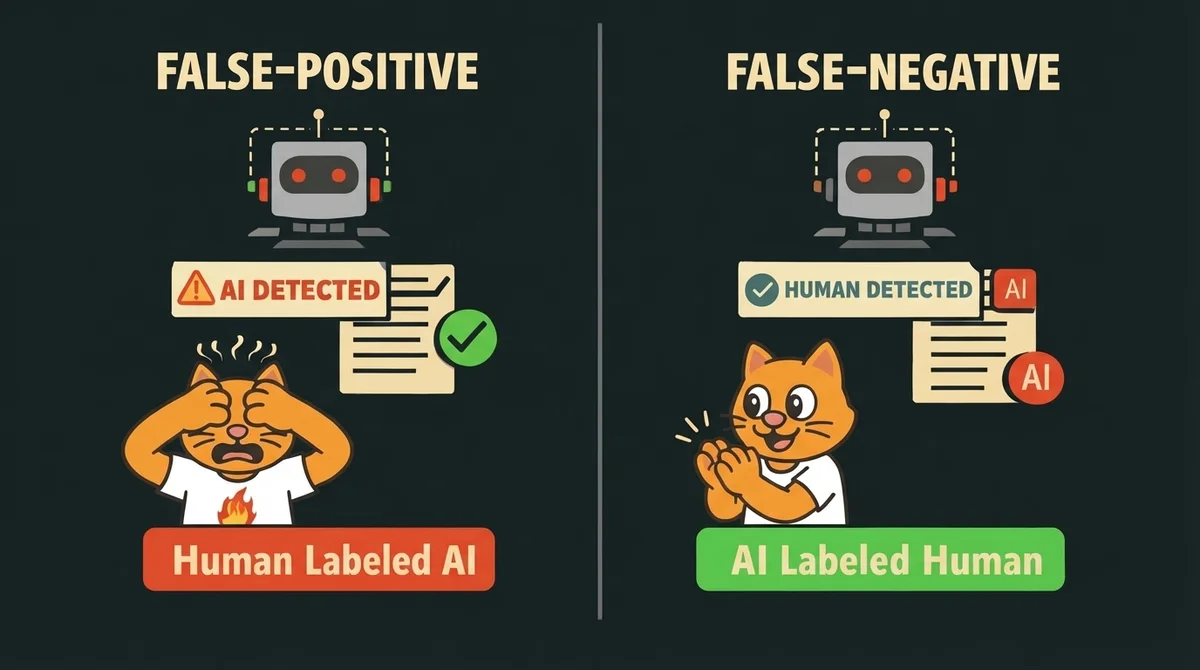
False positives occur when human writing mimics AI's statistical flatness. Academic rigidity, non-native speaker caution, and over-reliance on grammar tools like Grammarly trigger false positives.
This is the nightmare scenario for students… because academic writing is too predictable, too formal and too structured. It’s ironic, how we were taught to follow patterns to write clearly in school for ages, yet modern students are accused of using AI simply for being good students.The line between human vs AI text is blurred here.
False negatives happen through prompt engineering ("write with slang / idioms / use the style of some author,". Sometimes prompt engineers provide text samples to copy the style. Besides, if a human writes the draft and AI polishes it, or vice versa, the mixed signals confuse the classifier.
| Feature | False Positive Trigger (Human labeled as AI) | False Negative Trigger (AI labeled as Human) |
|---|---|---|
| Sentence Structure | Rigid, formal, repetitive academic syntax. | Deliberately introduced grammar errors or run-on sentences. |
| Vocabulary | Limited vocabulary (often non-native speakers). | High usage of slang, idioms, or niche jargon. |
| Consistency | Extremely polished editing (e.g., Grammarly overuse). | inserting personal anecdotes or emotional irrationality. |
| Length | Very short snippets (<100 words). | Heavily paraphrased or "humanized" content. |
Beyond Text: Image, Audio & Video AI Detection
In 2026, text is just the tip of the iceberg. The internet is flooded with synthetic media. To detect AI images or check for deepfakes requires a different set of technological eyes.
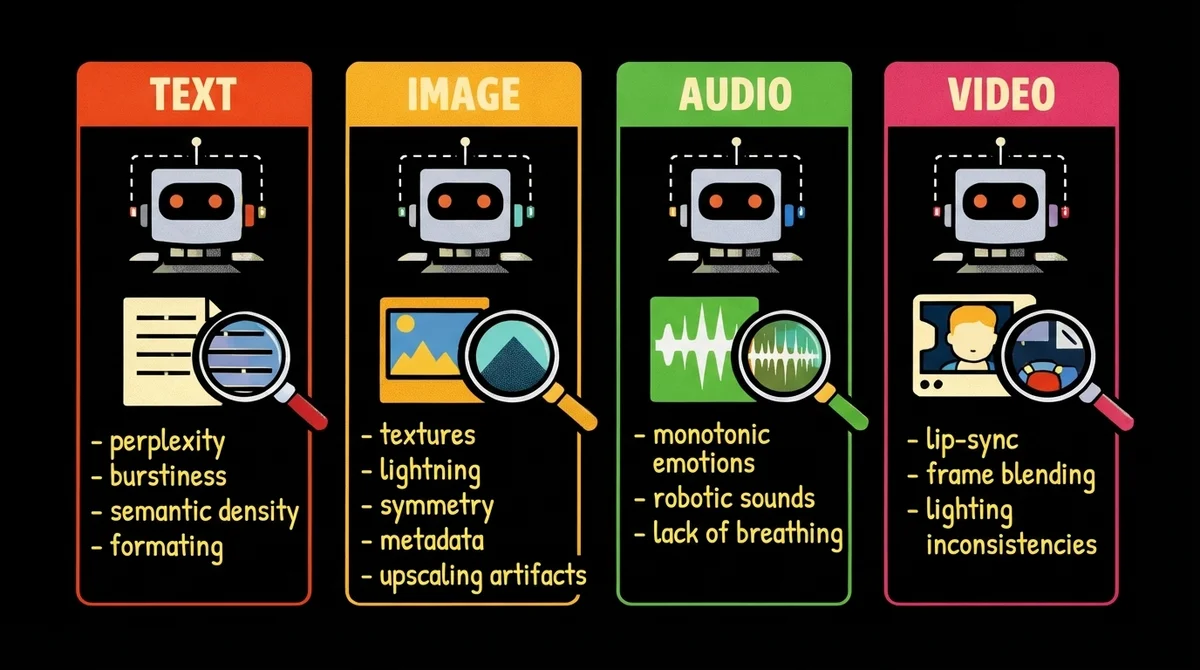
Image Detection
An AI image detector analyzes the raw pixel data. While humans look at the "picture," the detector looks at the noise. Upscaling artifacts, lighting physics inconsistencies, and metadata watermarks reveal AI origin.
Audio Detection
To detect AI audio, tools analyze the waveform and spectrogram. AI voices lack micro-variations in breathing, mouth clicks, and high-frequency data that real recordings contain. Spectral cutoffs and monotonic emotion patterns signal synthesis.
Video / Deepfake Detection
An ai video detector or deepfake video detector is the most computationally expensive tool. It looks for temporal inconsistencies. Believe it or not, video detectors can see the subtle color changes in skin caused by your heartbeat (photoplethysmography). Frame-by-frame analysis often reveals that lip movements don't perfectly align with the phonemes of the audio, or that blinking patterns are statistically irregular.
isFake.ai is a multimodal AI detection platform analyzing text, images, audio, and video. Instead of giving a binary verdict, it provides probability scores and explains which signals were detected. This makes it suitable for journalists, educators, researchers, and teams who need reliable content authenticity checks.
Can You Trick an AI Detector? (Reality Check)
Users often search for a free AI text detector hoping to find a way to bypass it. They ask how to make AI text more human. Paraphrasing tools can lower scores by introducing errors and synonyms. However, sophisticated detectors now recognize "humanizer" fingerprints.
The only reliable approach is to use best AI text detectors for outlining, but write sentences yourself, add unique anecdotes, and include recent facts the model shouldn't know. To check if text is AI, tools look deeper than surface-level synonyms. They analyze the logic flow.
Practical Tips for Writers, Students, Journalists
- For writers. Don't be afraid of AI, but use it for brainstorming, then rewrite the output.
- For students. Check your paper using AI detectors and then edit highlighting sections to add a voice.
- For journalists. Never rely on a single tool (and on a single source) for verifying images or video. Cross-reference images, use reverse image searches and source verification.
Try AI detection in practice with isFake.ai. isFake.ai offers text, image, audio and video detectors with detailed explanations of flagged signals, probability scoring and multimodal analysis. It is designed to help users verify content authenticity across formats — from essays to deepfakes.


